Table of Contents
ToggleIndonesia has a legal basis in Article 23A of the 1945 Constitution (UUD 1945) for corporate income tax.
There are various types of tax in Indonesia, especially for corporates. If you are a foreigner planning to open a business, it is important to understand them. Here’s the tax information in Indonesia that you must know:
Corporate Income tax in Bali and Indonesia
Taxation in Indonesia for resident corporations is subject to taxation on their global income. Foreign companies engaging in business through a permanent establishment (PE) in Indonesia assume similar tax obligations as resident taxpayers.
The corporate income tax in Indonesia is set at 22% of the net profit. However new companies or certain sectors might benefit from a certain tax regime.
Enjoy tax advantages tailored for small enterprises
Corporate taxpayers with an annual turnover of up to 50 billion rupiah (IDR) are eligible for a 50% tax discount from the standard rate. This discounted rate applies proportionally to taxable income on the portion of gross turnover up to IDR 4.8 billion.
Enterprises with a gross turnover not exceeding IDR 4.8 billion are subject to a final income tax rate of 0.5% based on turnover. Particularly of the regime, taxpayers are required to install the CIT on a monthly basis with self-assessment principle.
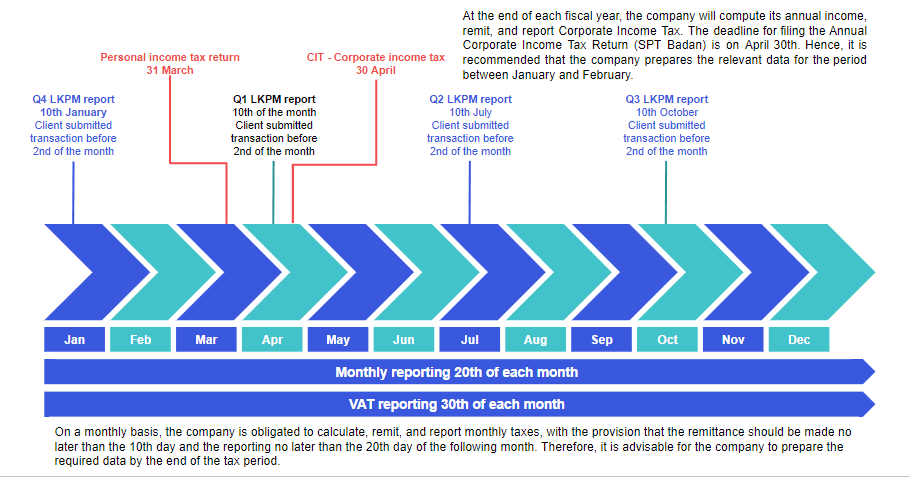
Therefore, tax planning is necessary because the Annual Income Tax Return (SPT) must be submitted no later than the end of April of the following tax year.
Branch Taxation in Indonesia
Branch Profit Tax (BPT) is an additional tax imposed on a Permanent Establishment (PE), complementing the Corporate Income Tax (CIT). The BPT rate stands at 20% and is levied on the PE’s net profit. However, this rate may be subject to reduction based on the statement of a tax treaty between where the Branch is tax resident. Notably, an exemption from Branch Profit Tax is granted if the net profit after tax of the PE is reinvested in Indonesia, provided it meets specific requirements. This provision serves as an incentive for strategic reinvestment in the Indonesian business landscape.
Never worry about taxes and accounting again
Dealing with finances, taxes, and accounting can feel overwhelming, especially as a foreigner in Indonesia. Let us guide you through processes like tax calculation, payroll, personal or corporate tax, short-term investments, balance sheet analysis and much more.
With ILA by your side, nothing can go wrong. Schedule a free consultation today or learn more about our tax and accounting services.
Corporate Income Tax Payments and Deadlines in Indonesia
Understanding Deductible and Non-Deductible Business Expenses in Indonesia
A company starting in Indonesia has the first 3 years no advantages with deductible expenses. Indeed, the tax office applies the tax on the income and not on the net profit. However it is still important to record the expenses in order to maintain the balance sheet and PnL (profit and loss) of the company to fill the LKPM report out every quarter.
Most of expenses of the company are deductibles. It includes:
- salaries
- rent
- donations
- expenses related to the business activity
However, the tax office doesn’t recognize the expenses below as deductible:
- rent for private use
- taxes and penalties
- reimbursement for an employee if the expense is not related to the activity of the company (to avoid the withholding tax and tax on salary)
Read also: Dubai to Bali : Tax Treaty Indonesia and UAE
Other taxes
Regional Taxes
Corporate taxpayers may incur various regional taxes and retributions, with rates spanning from a minimum of 0.2% to a maximum of 75%. These rates are applied to a diverse set of reference values established by the respective regional governments. Businesses such as hotels, restaurants, villas, renters, spas, fitness centers have to pay a local tax called PB1. The rate is variable in instance from 10 to 12.5%.
Import tax in Indonesia
Luxury tax on import goods in Indonesia
Despite a regulation from 2021 certain products are still subject to a luxury tax in Indonesia. This tax usually applies on top of the VAT.
Import duty
Importer or resident companies have to face import duty on top of the VAT. HS codes are primordial to determine the correct tax amount.
Withholding tax on payment
Particularly the Indonesian tax system requires that a taxpayer pays a tax on a payment done to another taxpayer. The party A buying a service or paying a dividend to another taxpayer needs to withhold a tax and requires the tax number of the second party to pay on its behalf. This amount is from 2 to 10% based on the type of payment.
Taxpayers are subject to withhold a tax of 20% for any payment made to non resident. Transfer pricing is important to be planned in advance to optimize the tax payment.
Read also: Tax Planning: How to Optimise Taxation in Indonesia
Capital gain and Interest rate
The system treats capital gain as income and applies the tax regulations described above. A withholding tax rate of 15% applies on the gross amount of interest. The WHT applied domestically on this interest serves as a tax credit, offsetting against the standard income tax rates of 22% for corporate taxpayers.
VAT in Indonesia
The Value Added Tax (VAT) law in Indonesia permits the government to adjust the VAT rate between 5% and 15%. As of April 1, 2022, the applicable VAT rate on deliveries of goods and services within Indonesia is 11%, with exceptions.
Companies can export at 0% while the import of goods incurs an 11% VAT. Certain services related to movable and immovable goods outside the Customs Area fall under 0% VAT, including toll manufacturing, repair services, and consultation for construction.
Services performed within the Customs Area for customers outside are subject to the standard 11% VAT. Consumption of foreign services and intangible goods, delivered via e-commerce to users in Indonesia, incurs an 11% VAT. The VAT is due on the accrual principle goods when the company delivers the goods or services . VAT filing is a monthly requirement, with payment and filing due by the last day of the month following the taxable delivery.
With regulations on taxes in Indonesia, it is certainly a concern for those of you starting a business in the country. Contact us to receive financial and tax advisory services that can facilitate the operation of your business.